
There is a bevy of heat pump makers in the HVAC industry, but Goodman owns a sizeable share. This is due to its warranty program and overall reliability. This is why HVAC.com ranks it as the best heat pump brand of 2020. Before seeing the list of the best Goodman heat pump models on the market, you should ask yourself how can a Goodman heat pump be of benefit to me?
Goodman heat pumps are designed to provide cooling in summer and heat in winter, throughout the year. These state-of-the-art heat pumps with inverter technology do not produce heat from the combustion of a fuel such as gas or diesel. They simply work through minimal electricity consumption, taking advantage of the energy from the air, and transferring it to your home. In our review of the best Goodman heat pumps, factors considered are various features such as the dimensions, speeds, SEER, EER, HSPF, BTU, tonnage, and more. Continue reading to discover more in the reviews and the buying guide.
Do you need an efficient split system to cool and heat your home all year round? The Goodman GSZ140361 and the ARUF37D14 are the right combinations of thermal equipment you need. The product includes a heat pump and an air handler.
The aerothermal heat pump uses a completely clean technology. It is capable of obtaining from outside air up to 79% of the energy provided to heat the home. The Goodman 14 seer heat pump provides efficient energy and minimal noise levels, which make the product one of the best cooling and heating equipment. The Goodman 3 ton heat pump features an R-410A refrigerant that is free of chlorine and a very efficient scroll compressor. It incorporates the SmartShift® technology. This is an innovation that ensures quiet and reliable defrosting. Also, there’s a factory-installed filter drier, accumulator, compressor heater, muffler, low and high-pressure switches. The heat pump is listed by Intertek’s Electrical Testing Labs (ETL) and also certified by the Air Conditioning, Heating & Refrigeration Institute (AHRI).
As for the air handler, it can be used for refrigerants R-22 (colorful gas known as chlorodifluoromethane) and R-410A (containing difluoromethane and pentafluoroethane). The air handler’s evaporator coil is entirely made of aluminum. This equipment is also AHRI-certified and ETL-listed.
The product is built of very reliable materials. The cabinets are made of galvanized steel materials that are fully insulated. This is finished with grain-embossed leather.
What we liked: As is offered in all Goodman products, the equipment comes with 10 years of warranty on the parts. This is provided and installed by a registered and qualified installer. We also like the fact that it is certified and listed by industry-standard testing labs and HVAC institutes.
What could be better: It’s not easy to install by a DIYer. Even if you can, and you do, then the warranty will be voided, according to the maker.
The Goodman GSZ140301 is a heat pump with an energy efficiency ratio (EER) of 11.5 and a seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER) of 14. This ensures you have efficient comfort irrespective of its application and period of use. The Goodman 2.5 ton heat pump can cool and heat the air. It has a cooling power rated at 3000 British thermal units (BTU). Meanwhile, the heating power is rated at 24000 BTU.
The 252 voltage heat pump has a condenser coil which is made of aluminum fins as well as copper tubing. This helps maximize its overall efficiency. The heat pump includes a condenser fan and a louvered top which reduce the noise levels of the unit, while not reducing its performance. The discharge muffler also helps to decrease its vibrational noise to the bare minimum. The pump’s liquid line features a filter drier that traps impurities and reduces moisture. This also prevents corrosion, blockages, and freezing during winter.
What we liked: Despite the high-efficiency ratios of the heat pump, we like how quiet it can be. Also, it has 14 nominal SEER value.
What could be better: There is no problem with this heat pump. It’s a steal for its price.
Goodman makes the GPH14M available at a very competitive price, while not compromising the quality. This heat pump delivers high-efficiency performance. Indeed, when you compare the heat pump with the Goodman GSZ140361 and the Goodman GSZ140301, it performs much better in terms of the nominal efficiency values. It has an energy efficiency value (EER) of 11, almost the same as the former. Also, it has a seasonal energy efficiency value of 14, the same as the former. However, it beats the two in the heating and cooling capacity. The Goodman GPH14M is a 4-ton heat pump that has a cooling power rated at 36,400 BTU (the second model has 30,000) and heating power of 26,600 BTU (the second model has 24000).
The Goodman 4 ton heat pump is a comfort solution recommended by verified users and suitable for all residential applications. The unit features a heat pump, ECM blower, and evaporator coil all in one single unit, which is why it’s able to provide more efficient cooling and heating power.
What we liked: The Goodman heat pump package unit is an all-in-one system that includes an ECM blower and evaporator coil, while remaining more compact. The ECM blower saves energy while improving the overall performance of the unit. Its compact design also helps to save space.
What could be better: The aesthetic appearance of the heat pump could be better since it is an equipment used in and around the home. But this is excusable insofar as much as it performs its functions.
Choosing a Goodman heat pump, just like many other brands, is not an easy task. This is because they have quite a lot of models. Let this section guide you towards making the best purchasing decision.
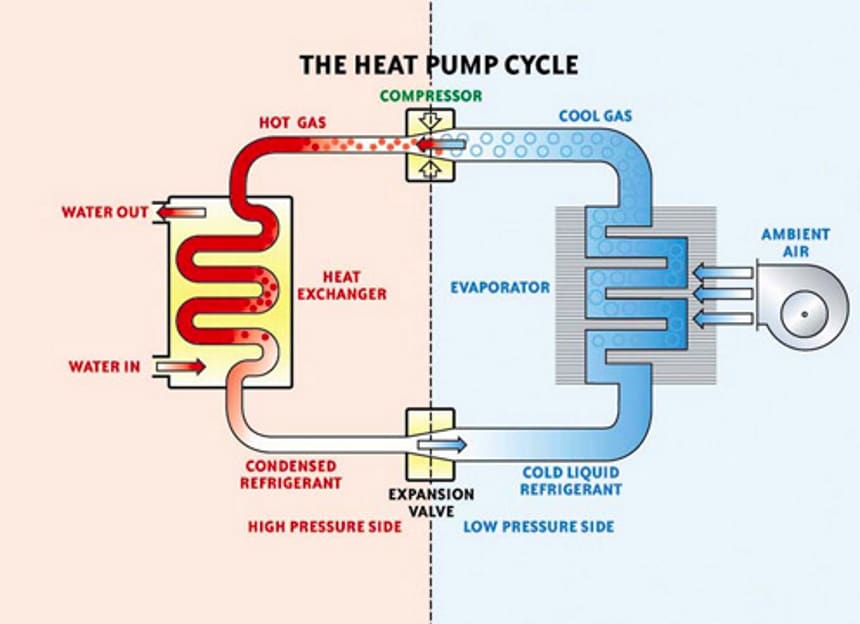
The interesting thing about the heat pump is that the amount of energy consumed in making the compressor work is small compared to the energy given off by the condenser. Comparing the power supplied to the compressor with the energy of the electric heating by the Joule effect, the heat pump supplies 4 times more useful heat, with the energy savings that this implies.
Goodman isn’t renowned as the best heat pump on the market for nothing. It offers property owners a wide variety of benefits towards an efficient heating and cooling functionality. Below are some of the advantages and disadvantages of buying a Goodman heat pump.
There are some important features to consider before buying a Goodman heat pump. From the EER and SEER ratings, HSPF, noise level, to the compressor, here we analyze them in full.
First we should consider the existing types of the heating pumps:
Heat pumps according to construction
Depending on the way in which the equipment is built, it can be:

Heat pumps according to operation
The dimensions of your heat pump are important, especially when you don’t have enough space. However, the good thing about Goodman models is that you can find compact models with equal functionality of bigger or split heat pumps. The average dimension of a heat pump is usually in 22″ Height, 32″ Width, and 1′ Depth. This dimension is smaller than an average air conditioning condenser.
The Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) and Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) are all energy performance parameters. They allow us to know the energy efficiency of a heat pump. These coefficients relate the amount of energy to be contributed to the system, that is, consumption, with the heat or cooling obtained from it. There is also the Coefficient of Performance (COP). This is the expression of the energy efficiency of a heat pump. In other words, it is the relationship between the power (kW) that comes out of it and the power (kW) that is supplied to the compressor that produces that heat.
The energy efficiency index or Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) also measures the relationship between the electrical energy consumed and the total power a heat pump generates. In 2013, Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) No. 626/2011 entered into force on the energy labeling of HVAC equipment. This fact meant a change in the denomination of the parameters that measure the energy efficiency of these devices. Thus, the current name is Seasonal Coefficient Of Performance (SCOP) and Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER).
In addition, from that moment on, the information that the labels must include that can be consulted in Annex III of said law was established. In this way, if your equipment is prior to 2013, the COP and EER parameters will be indicated, but if they are later, they will be SCOP and SEER. The EER and SEER parameters refer to the efficiency of the equipment in cold production, that is, refrigeration; and the COP and SCOP parameters refer to the energy efficiency of the equipment in heat production, that is, heating. The higher they are, the better the efficiency of the equipment, and generally its price will be higher.
The interesting thing is to find the balance between the ratio and the price. In the long term, cheap equipment with a very low SEER will be less efficient.
The basic difference between the EER-COP and the SEER-SCOP is that the latter are seasonal. The EER and the COP measure power under certain environmental conditions operating at full load; while SEER and SCOP measure seasonal energy performance taking into account:
In the event that you cannot find the data for the seasonal average yield (SCOP and SEER), you can find the default nominals, that is, COP and EER. But here are some tips to help you find them:

As mentioned in the product review, the BTU stands for British thermal units. Meanwhile, the CFM stands for cubic feet per minute. To choose the right BTU and CFM, choose a model with a CFM of 350-450 per 12000 BTU per hour capacity. Choose a model with at least 750 CFM for every 12000 BTU per hour across outdoor coils.
The heat pump compressor is an element that consumes mechanical energy for its operation. Its function is to increase the pressure of the refrigerant in the gaseous state, coming from the evaporator to a pressure that transforms that gas into a liquid. Depending on how the motor is coupled with the compressor there are different types:
The good thing about Goodman heat pumps is that they are ultraquiet. The GSZ line which the Goodman GSZ140361 and the Goodman GSZ140301 belong to emit noise level between 72-76 decibels. They have condenser fans which give good cooling effects and quiet air movement through the coils and blades.
There are other accessories that accompany the heat pump so that its refrigerant circuit remains in an optimal state. They are classified according to the pressure of the area where they are. In an installation, there are two main zones depending on the state of the refrigerant:
The following elements are found in the high-pressure zone of heat pumps:
In the low-pressure part, the following stand out:
The different certifications and regulations are indicators of quality, efficacy, and safety.
Installing your Goodman heat pump requires the service of a professional that is registered online. You’ll void the warranty if you install it yourself and you’re not a registered, certified professional installer.
Maintenance must be done by a qualified technician. You will also have to be careful that there is nothing that hinders the operation of the outdoor unit. Each time, maintenance efforts must be directed at the fins, the surrounding area, the condenser, evaporated coil, and the evaporator drain.
Goodman is arguably the best heat pump manufacturer on the planet. In the end, choosing their best products isn’t an easy task. Our overall best Goodman heat pump is the combination of the Goodman GSZ140361 and the ARUF37D14. Also, our Editor’s Choice, this Goodman split system heat pump is certified and listed by the industry’s top standard testing labs and HVAC institutes. The product includes a heat pump and an air handler for efficient heat and cool air generation. The winner of our Best Value nomination, the Goodman GPH14M delivers high-efficiency performance. Indeed, when you compare the heat pump with the Goodman GSZ140361 and the Goodman GSZ140301, it performs much better in terms of the nominal efficiency values. Finally, if you want the best Goodman heat pump that doesn’t cost an arm, choose our Budget Pick, the Goodman GSZ140301. This is a heat pump for cooling and heating the home. It has an energy efficiency ratio (EER) of 11.5 and a seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER) of 14. This ensures you have efficient comfort irrespective of its application and period of use.





